 Home » Chemical Review for Biology
Home » Chemical Review for BiologyKey Terms
Atoms:
- electrons: both energy and substance particles
- neutrons
- protons
Molecules:
- Formed by atoms
- Joined by chemical bonds
- molecular formula and structure formula
Organic Molecules/macromolecules:
- amino acids --> proteins
- monosacchrides --> polysaccharides
- fatty acids --> lipids
- nucleotides --> nucleic acids
Isotope: atoms have same proton numbers but may differ in neutron numbers
Energy shell: Electrons occupy orbital around nucleus, these are called energy shell. The most inner shell (K) contains 2 electron maximun, the L and M shell contain 8 maximum each.
Organic chemicals: chemicals are made from living organisms and contain carbon backbones.
Isomers: Chemicals that have same molecular formula but different structure formula.
Buffers: solutions which resist change in pH upon addition of small amounts of acid or base.
Electrolytes: chemicals that can release ions into solutions
pH: pH represents the concentration of hydrogen ions [H+] in solution.
pH = -log [H+]
Enzymes: proteins that serve as catalysts for biochemical reactions.
Enthropy: a measure for a system's degree of disorder. It increases with increasing disorder.
Law of thermodynamics:
- The first Law: The total energy of the universe is always conserved. Energy can neither be created nor destroyed.
- The second Law: The universe tends towards maximum disorder, or, in other words: the direction of all spontaneous processes is such as to increase the entropy of a system plus its surroundings
ΔG: Change of free energy of a system.
- ΔG negative reaction: spontaneous
- ΔG positive reaction: non-spontaneous
Chemical Bonds
Chemical bonds store energy. For covalent bonds, the more electrons a bond share, the more energy it stores.
Ion bond: ion bond forms when atoms lose or gain electrons.
Covalent bond: Covalent bonds form when atoms share electrons, very strong bonds. The major one in organic chemicals.
Hydrogen bond: Weak electrical attraction between the positive end of one molecule and the negative end of another
Organic Chemicals
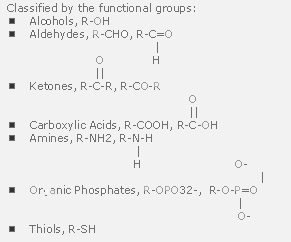
Important Biochemical Molecules
Organic Molecules/macromolecules:
- Polysaccharides
- Monomer unit: monosaccharide
- store energy, provide building unit
- Lipids
- Monomer unit: fatty acids, glycerol
- Store energy, membrane construction, hormones
- Proteins:
- Monomer unit: amino acids
- Structure protein, enzymes
- Nucleic Acids:
- Monomer unit: nucleotides
- Genetic material
Chemical Reactions
Coupled reactions: many biosynthesis reactions are coupled to ATP hydrolysis which can provide energy and therefore the overall reaction can be delta G negative.
- ΔG negative reaction: spontaneous
- ΔG positive reaction: non-spontaneous
Enzyme catalyzed reactions: lower the activation free energy but do not change the ΔG.
Biochemical Reaction Types and Enzymes
- Oxidation-reduction reactions: oxidoreductase
- Intramolecular or intermolecular functional group-transfer reactions: Transfease
- Hydrolysis of esters, ethers, and amides: hydrolase
- Elimination or addition reactions: Lyase.
- Isomerization reactions: isomerase
- Formation of ester, thiol ester, and amide linkages: Ligase