 Home » Genetics Basics
Home » Genetics BasicsKey Terms
Key molecules: DNA, RNA and protein
Key concepts:
- Gene
- the central dogma
- Genetic code
- Gene transmission
- Chromosome
Building units
DNA
A, Adenine
T, Thymidine
G, Guanine
C, Cytosine
RNA
A, Adenine
U, Uracil
G, Guanine
C, Cytosine
Protein
20 Amino Acids
DNA
- Is the cellular genetic material
- Made up from deoxyribose-phosphate and 4 bases
- Contains two strands based on base pairing between A and T, C and G.
- The two strands are anti-parallel and form double helix structure
- Highly organized in cells (final form: chromosome)
- One Chromosome contains one DNA molecule
- One chromosome contains many genes
- One gene is defined as one functional section of DNA
- Genes (DNA) only carry genetic information, which needs to be processed into RNA or protein to perform its biological function
RNA
A molecule made of a stretch of bases on a sugar-phosphate backbone
Sugar is ribose instead of dexoyribose in DNA
Bases are AUCG instead of ATCG in DNA
Smaller molecules
Single-stranded
mRNA: Copies information from DNA through base-paring mechanism and serves as an messenger from DNA to protein
tRNA: carries amino acid to protein synthesis place
rRNA: component for ribosome
ncRNA: regulate cellular processes
- Various functions:
- Making protein
- Regulate cellular process
- Component for certain cellular structure
Protein
- Made out of 20 amino acids
- Encoded by genes, one gene, one protein.
- Required for all cellular process
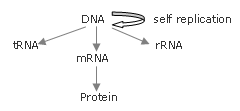
The Central Dogma
The Genetic Code
- mRNA is read from an initiation codon
- Triplet code: every three bases encode one amino acid or a stop codon
- One amino acid can be encoded by multiple codons
- The base sequence is read consecutively
Gene Transmission
DNA is self-replicated
Duplicated DNA is packed into duplicated chromosomes
Duplicated chromosome segregate evenly into two chromosomes
Cell is divided into two, each containing one set of crhomosomes
Mutations and Genetic Disease
Mutations: changes in DNA sequence, i.e., insertion/deletion.
- Causes:
- errors during DNA replication
- DNA damage
- Chromosome errors
- Consequence: malfunctioned gene product
- Phenotype:
- somatic mutation: non-inheritable disease
- Germ line mutation: genetic disease
Gene Therapy
Genetic disease can be corrected by introducing a functional copy of gene into the affected tissues.