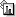 Home » Molecular Biology At-A-Glance
Home » Molecular Biology At-A-Glance
Key Terms
Molecular Biology is the study of the replication,
transcription, & translation of genetic material within a cell. Manipulation of these processes is also known
as molecular biology or recombinant DNA techniques.
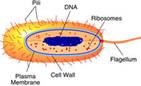
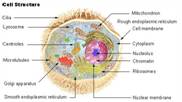
Macromolecules- there are four main classes of macromolecules: lipids, proteins, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids.
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)- double helix chains of paired bases containing thymine, cytosine, guanine, and adenine.
Ribonucleic acid (RNA)- the intermediate between DNA and proteins.
Proteins- chains of amino acids coded for by genes in the DNA.
Transcription
DNA is transcribed into RNA and special pairing of bases dictates which sequence is made.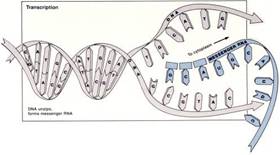
Translation
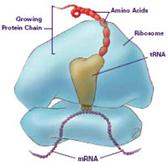
Gene Expression
Important DNA Processes
DNA replication- is the process in which a strand of DNA makes an identical copy of itself.
DNA repair- a complex set of enzymes proofread DNA and repair brakes in the double helix.
DNA recombination- is the mixing of genetic material from two chromosomes as a result of crossing over.
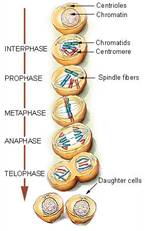
Cell Division
Interphase– duplication of genetic material.
Prophase– condensation of chromatin into chromosomes.
Metaphase– binding of chromosomes to mitotic spindle.
Anaphase– separation of chromosomes into opposite sides of the cell.
Telophase– reformation of cell and nuclear membranes.
Cytoskeleton Components
The cytoskeleton gives cells structure and is composed of three types fibers:
Actin– composed of actin polymes, important for cellular locomotion and contraction of muscle cells.
Microtubules– composed of tubulin poymers, important for vesicle motilty and separation of chromosones during cell division.
Intermediate filaments– composed of proteins such as keratin and lamin, important for cell adhesion and signaling.
Membrane Transport
Simple diffusion– passive transport down with rate determined by a molecules permeability, size, and concentration gradient
Facilitated diffusion– carrier protein mediated but does not use energy
Active transport– uses both carrier proteins and metabolic energy, can move molecules against an electrochemical gradient (i.e. uphill)
Cotransport – uses a carrier protein to move two molecules the same direction across a membrane without metabolic energy. One molecule (usually sodium) move “downhill” and the other “uphill”
Countertransport - uses a carrier protein to move two molecules the opposite direction across a membrane without metabolic energy