 Home » Ecology Overview
Home » Ecology OverviewKey Terms
Community: All the organisms that inhabit a particular area. An assemblage of populations of different species living close enough together for potential interaction.
Ecosystem: A level of ecological study that includes all the organisms in a given area along with the abiotic factors with which they interact. A community and its physical environment.
Producers: They are primarily green plants that bring energy into the system by capturing sunlight.
Producers: They are primarily green plants that bring energy into the system by capturing sunlight.
Consumer: An organism in an ecosystem that lives by eating other organisms.
Consumers: An organism in an eco system that lives by eating other organisms.
Decomposers: Saprophytic fungi and bacteria that absorb nutrients from non-living organic material such as corpses, fallen plant material and the waste of living organism and convert them into inorganic forms.
Biosphere: The entire portion of the earth that is inhabited by life. The sum of all the planet’s ecosystems.
Biomes: The world’s major communities classified according to the predominant vegetation and characterized by adaptations of organisms to that particular environment.
Population: A group of individuals in a particular geographic area that belong the same species.
Endotherms: Animals that use metabolic energy to maintain a constant body temperature.
Regulators: They are able to maintain constant internal conditions when the external environment changes.
Conformers: They cannot regulate their internal environment which varies to match the external environment.
Acclimation: Physiological adjustment to a change in an environmental factor.
Chaparral: Dense spring shrubs with though ever green leaves.
Niche: The sum total of an organism’s utilization of the biotic and abiotic resources of its environment.
Habitat: The immediate environment of a living organism.
Biotic: Pertaining to the living organisms in the environment.
Abiotic: Pertaining to the non-living factors which are physical and chemical components.
Temperature: A measure of the intensity of heat in degrees reflecting the average kinetic energy of the molecules.
Savanna: It is the tropical or semitropical grassland with scattered individual trees.
Taiga: It is the coniferous or boreal forest found at higher elevations in more temperate latitudes.
Tundra: A biome at the northernmost limits of plant growth and at high altitudes, where plant forms are limited to low shrubby or matlike vegetation.
Permafrost: Continuously frozen ground that prevents roots of plants from penetrating very far into the soils. Found in arctic tundra region.
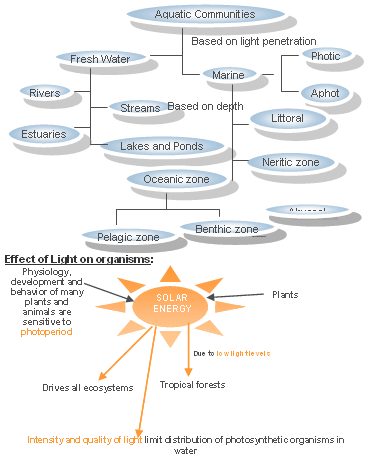
Estuaries: The area at which a fresh water river or stream meets the ocean is called an estuary.
Lianas: Vines growing rapidly when an opening does occur in the tropical rain forest.
Photic zone: The narrow top slice of the ocean where light penetrates sufficiently for photosynthesis to occur.
Intertidal zone: The shallow zone of the ocean where land meets water. Also called the littoral zone.
Neritic zone: The shallow regions of the ocean overlying the continental shelves.
Pelagic zone: The area of the ocean past the continental shelf, with areas of open water often reaching to very great depths.
Benthic zone: The bottom surfaces of the ocean.
Abyssal zone: The portion of the ocean floor where light does not penetrate and where temperatures are cold and pressures intense.
An overview of the concept map of ecology
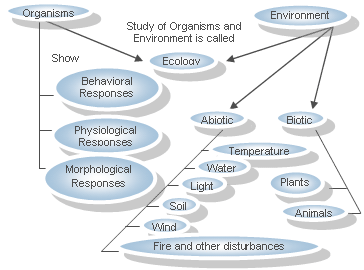
Three distinct mechanisms responding to changing environments
1. Behavioral
2. Physiological
3. Morphological
Classification of aquatic communities