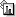 Home » Macromolecule Concept Map
Home » Macromolecule Concept MapKey Terms
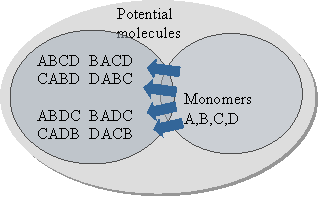
Macromolecule: A molecule having a molecular weight in the range of a few thousands to many millions.
Functional group: The specific atom or group of atoms that confers a particular chemical property on a biomolecule.
Organic Compounds: Molecules containing covalently bonded carbon backbones are called organic compounds.
Hydrolysis: Cleavage of a bond, such as an anhydride or peptide bond, by the addition of the elements of water, yielding two or more products.
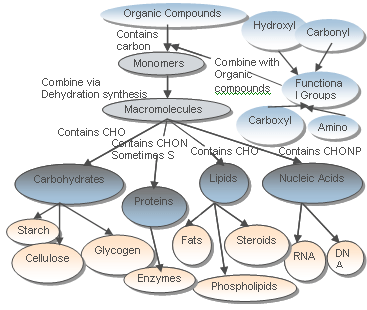
Monosaccharide: A carbohydrate consisting of a single sugar unit.
Disaccharide: A carbohydrate consisiting of two covalently joined monosaccharide units.
Polysaccharide: A linear or branched polymer of monosaccharide units linked by glycosidic bonds.
Protein: A macromolecule composed of one or more polypeptide chains, each with a characteristic sequence of amino acids linked by peptide bonds.
Amino acids: Alpha amino-substituted carboxylic acids, the building blocks of proteins.
Primary structure: A description of the covalent backbone of a poymer, including the sequence of monomeric subunits and any interchain and intrachain covalent bonds.
Secondary structure: The residue by-residue conformation of the backbone of a polymer.
Tertiary structure: The three-dimensional conformationof a polymer in its native folded state.
Quaternary structure: The three dimensional structure of a multisubunit protein; particularly the manner in which the subunits fit together.
Fatty acid: A long chain aliphatic carboxylic acid found in natural fats and oils.
Fat: An ester of fatty acids with glycerol as the alcohol.
Lipid: A small water- insoluble biomolecule generally containing fatty acids, sterols or isoprenoid compounds.
Sterols: A class of lipids containing the steroid nucleus.
Nucleoside: A compound consisiting of a purine or pyrimidine base covalently linked to a pentose.
Nucleotide: A nucleoside phosphorylated at one of its pentose hydroxyl grups.
Nucleic acids: Biologically, occurring polynucleotides in which the nucleotide residues are linked in a specific sequence by phosphodiester bonds. DNA and RNA.
DIVERSITY:
A few monomers can combine to create a lot of combinations.
Concept Map of Macromolecules
Carbohydrate Table
Protein Structure
