 Home » Mitosis and Meiosis
Home » Mitosis and MeiosisKey Terms
Cell skeleton: Composed of microtubules made of tubulin and actin, plays roles in maintaining cell shape, cell motion, intra-cellular transport and cell division –both mitosis and meiosis.
Centrosome: Made of two centrioles, it is the main microtubule organizing center (MTOC) and a regulator of cell-cycle progression.
Mitotic spindle: A dynamic protein structure assembled at early mitosis stage, consisting of a bundle of microtubules joined at the ends but spread out in the middle. The function is to pull chromosomes to two opposite poles.
Kinetochore: The protein structure assembled on the centromere and links the chromosome to microtubules from the mitotic spindle.
Diploid Number (2N): The total number of chromosomes present in a somatic cell containing 1 pair of homologous chromosomes.
C Value: The total amount of DNA in a haploid cell.
Cytokinesis: The division of the cytoplasm in a cell, which usually occurs immediately after nuclear division in mitosis.
Sister chromatid: Two identical chromatids after chromosome replication, stay together at the early stage of mitosis but separate later.
Cell cycle: Eukaryotic cells keep dividing, the series of events between one cell division and the next is termed cell cycle, normally containing G1, S, G2 and M (mitosis) phases.
Mitosis: The series events when a somatic cell is divided into two identical daughter cell. It normally contains prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase.
Meiosis: The series events when a cell is divided twice while its DNA only replicate once, resulting 4 haploid progeny cells –germ cells.
Synapsis: a pair of homologous chromosomes lines up closely together
Tetrad: A tetrad is composed of four chromatids, 2 sister chromatids from each of the homologous chromosomes
Mitosis
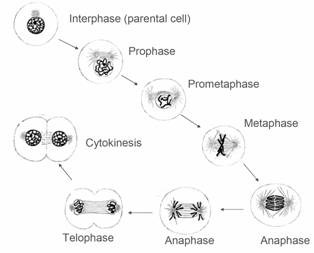
- DNA replicates once and cell divides once
- Sister chromosomes separate
- Resulting daughter cells contain one set of homologous chromosomes each
Meiosis
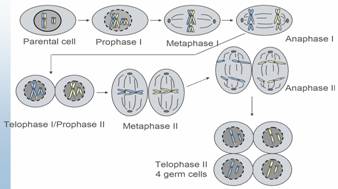
Stages of Mitosis and Meiosis
Prophase:
- Chromatin condense to form chromosomes
- Nucleolus disappears
- Centrosomes are duplicated and begin moving to opposite poles
- Formation of mitotic spindle
Prometaphase (for mitosis only):
- The nuclear membrane starts to dissolve
- Kinetochores formation
- Microtubules from spindles attach at the kinetochores and the chromosomes begin moving
Metaphase:
- Chromosomes are aligned on the metaphase plate
Anaphase:
- The sister chromotids separate at the kinetochores (for mitosis); Homologous chromosome separate (meiosis anaphase I) or sister chromosome separate (meiosis anaphase II)
- The separated chromosomes move to opposite sides of the cell.
Telophase:
- New membranes form around the daughter nuclei.
- The chromosomes disperse and are no longer visible under the light microscope.
- The spindle disembles
- Cytokinesis occurs
The Major Difference
Mitosis:
For somatic cell proliferation
Meiosis:
For germ cell production